Institutional investors, custodians, and enterprises must balance transaction costs, compliance, and security while ensuring efficiency. Understanding the unspent transaction output (UTXO) system is crucial for optimizing fees and performance.
This article examines Bitcoin’s UTXO model, outlines best practices for consolidation, and explains how advanced digital asset custody solutions can enhance UTXO management, ensuring that on-chain transactions remain secure, compliant, and cost-effective.
Understanding UTXOs
A UTXO is an indivisible portion of Bitcoin that a user has received and not yet spent. Unlike traditional banking systems that operate on a centralized Account Model, the UTXO model ensures decentralization by allowing nodes to validate transactions based on prior outputs independently.
This structure enhances Bitcoin’s transparency, security, and immutability.
Key Components of Bitcoin Transactions
-
Inputs: References to previous UTXOs used to fund a new transaction.
-
Outputs: Newly created UTXOs specifying the recipient's address and the amount transferred.
-
Coinbase Transactions: Special transactions at the start of each block, issuing newly mined Bitcoin to miners with no prior input.
Key Components of Each UTXO
-
Fixed Value: Each UTXO has a predetermined amount of Bitcoin.
-
Bitcoin Address Association: It is tied to a specific Bitcoin address.
-
Origin Transaction ID: It includes the transaction ID from the transaction that created the UTXO.
UTXO vs. Account-Based Models
The UTXO Model (Stateless)
UTXOs function like cash, where each unit is uniquely identified. Transactions require selecting specific UTXOs, similar to using bills and receiving change. Managing UTXOs efficiently is key, as more UTXOs increase transaction complexity.
Account-Based Model (Stateful)
Popularized by Ethereum and similar platforms, the account-based model aggregates balances like a traditional bank account without tracking individual tokens. This approach enables robust smart contract interactions for sophisticated decentralized applications (dApps) but relies on nonces to prevent duplicate transactions and careful handling of parallel processes.
For custody wallets with multiple receiving addresses, consolidation may be necessary to enhance operational efficiency and maintain security.
Why UTXO Management Matters for Institutions
Poorly managed UTXOs can result in increased transaction fees, privacy concerns, and operational inefficiencies.
The Impact of UTXO Management on Fees
Bitcoin transactions incur fees based on the data size of the transaction, measured in satoshis per virtual byte (sats/vbyte) rather than the financial value of the transaction. Fees rise in periods of network congestion, making it crucial to manage UTXO sizes efficiently.
For instance:
P2PKH Input Size (148 vbytes):
A standard Pay-to-PubKey-Hash (P2PKH) input consumes 148 vbytes.
Taproot Input Efficiency:
A Taproot input is more efficient, requiring only 57.5 vbytes.
Taproot is an activated soft fork change to Bitcoin that allows payments to schnorr public keys that may optionally commit to a script that can be revealed at spend time.
If network fees reach 200 sats/vbyte, then small UTXOs may become uneconomical, as fees could exceed the value of the UTXO itself (so-called "dust" UTXOs).
Dust UTXOs and Fee Considerations:
Without proper management, institutions risk accumulating small, inefficient UTXOs that cost more in fees than their actual value. As Bitcoininfocharts.com demonstrates below, you can see below, fees can vary greatly.
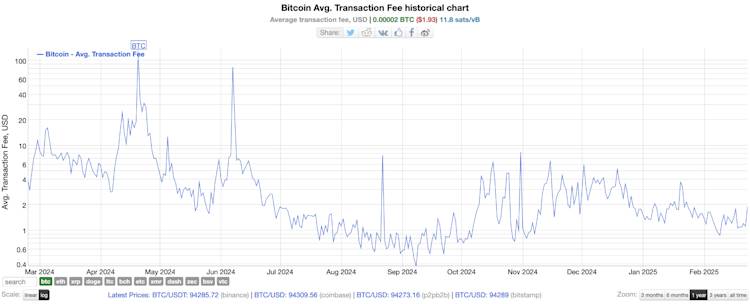
Best Practices for Institutional UTXO Management
Maintain Economically Viable UTXO Sizes
Ensure each UTXO is at least 1 million satoshis (0.01 BTC) to remain viable even in high-fee environments. Avoid accumulation of excessive small UTXOs, which may become unspendable due to transaction fees.
Balance Consolidation with Privacy Considerations
Consolidate UTXOs during periods of low fees to reduce future transaction costs. Avoid overconsolidation, which can expose the institution’s total holdings and weaken on-chain privacy.
Diversify UTXO Holdings for Flexibility
Maintain a mix of UTXO sizes to allow for optimal input selection in future transactions. Utilize API solutions for automated UTXO selection based on real-time network conditions.
Implement Segregation Strategies for Enhanced Privacy
Separate UTXOs based on funding sources (e.g., regulatory-compliant vs. non-KYC sources). Use dedicated addresses for different operational purposes to prevent unnecessary linking of transactions.
Time Transactions for Optimal Cost Efficiency
Monitor mempool congestion and initiate transactions when fee rates are lower. Utilize dynamic fee estimation tools to optimize transaction costs.
Utilize Layer 2 Solutions for Frequent Small Transactions
Reduce reliance on expensive on-chain transactions by leveraging the Lightning Network. Lightning allows for near-instant, low-cost Bitcoin transactions without occupying blockchain space.
Bitcoin with BitGo
BitGo supports multi-recipient transactions directly from its user interface, a feature previously available only to SDK users. This enhancement streamlines UTXO wallet management, making it more efficient for users.
Instead of creating separate transactions for each recipient, users can now send funds to multiple addresses in a single transaction, significantly reducing time and transaction fees. This update improves both cost efficiency and convenience for BitGo clients.
For more information on how BitGo can help your institution optimize its UTXO management, connect with us.
Table of Contents
- Understanding UTXOs
- Key Components of Bitcoin Transactions
- Key Components of Each UTXO
- UTXO vs. Account-Based Models
- Why UTXO Management Matters for Institutions
- The Impact of UTXO Management on Fees
- Best Practices for Institutional UTXO Management
- Maintain Economically Viable UTXO Sizes
- Balance Consolidation with Privacy Considerations
- Diversify UTXO Holdings for Flexibility
- Implement Segregation Strategies for Enhanced Privacy
- Time Transactions for Optimal Cost Efficiency
- Utilize Layer 2 Solutions for Frequent Small Transactions
- Bitcoin with BitGo
The latest
All NewsAbout BitGo
BitGo is the leading infrastructure provider of digital asset solutions, delivering custody, wallets, staking, trading, financing, and settlement services from regulated cold storage. Since our founding in 2013, we have focused on enabling our clients to securely navigate the digital asset space. With a large global presence through multiple regulated entities, BitGo serves thousands of institutions, including many of the industry's top brands, exchanges, and platforms, as well as millions of retail investors worldwide. As the operational backbone of the digital economy, BitGo handles a significant portion of Bitcoin network transactions and is the largest independent digital asset custodian, and staking provider, in the world. For more information, visit www.bitgo.com.
©2025 BitGo Inc. (collectively with its affiliates and subsidiaries, “BitGo”). All rights reserved. BitGo Trust Company, Inc., BitGo Inc., and BitGo Prime LLC are separately operated, wholly-owned subsidiaries of BitGo Holdings, Inc., a Delaware corporation headquartered in Palo Alto, CA. No legal, tax, investment, or other advice is provided by any BitGo entity. Please consult your legal/tax/investment professional for questions about your specific circumstances. Digital asset holdings involve a high degree of risk, and can fluctuate greatly on any given day. Accordingly, your digital asset holdings may be subject to large swings in value and may even become worthless. The information provided herein is not intended for distribution to, or use by, any person or entity in any jurisdiction or country where such distribution or use would be contrary to law or regulation. BitGo is not directing this information to any person in any jurisdiction where the publication or availability of the information is prohibited, by reason of that person’s citizenship, residence or otherwise.




